The compound fertilizer ammonium phosphate granulation production line is a type of equipment used for producing compound fertilizers. Here is a brief introduction to its working principles, main equipment, and process flow.
Description
- Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line for Compound Fertilizers
- I. Working Principles
- II. Key Equipment
- III. Process Flow
- IV. Features of the Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line
- V. Application Fields of the Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line
- VI. Key Selection Points for the Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line
Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line for Compound Fertilizers
An ammonia-acid granulation production line is a set of equipment that produces compound fertilizers. Here is a brief introduction to its working principles, key equipment, and process flow.
I. Working Principles
- Neutralization Reaction: It uses a neutralization reaction between liquid ammonia and acidic substances like sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid. For example, ammonia water reacts with sulfuric acid to produce ammonium sulfate, and this reaction releases a large amount of heat.
- Binding and Granulation: The high-temperature ammonium sulfate solution or other complex salt solutions from the reaction have a high viscosity. They act as a binder, binding powdered materials like potassium chloride, monoammonium phosphate, and urea into granules in the granulator.
- Complex Salt Formation and Solidification: During granulation, various raw materials also undergo complex chemical reactions, producing complex salts like potassium ammonium sulfate, potassium ammonium phosphate, and potassium ammonium chloride. These complex salts ultimately form a solid solution that solidifies the granules and increases their strength.
II. Key Equipment
- Ammonia Station Equipment: This includes a liquid ammonia tank, ammonia unloading booster, ammonia evaporator, gaseous ammonia tank, ammonia station pipeline valves, and flow meters. These units store, pressurize, and evaporate liquid ammonia and then transport gaseous ammonia to the reaction system.
- Acid Station Equipment: This includes a sulfuric acid storage tank, sulfuric acid pump, sulfuric acid flow meter, dissolution tank, slurry pump, acid mixing tank, acid mixing pump, intermediate tank, slurry spraying pump, acid mixing flow meter, tail gas fan, tail gas absorption unit, scrubbing liquid circulation pump, and pipeline valves. They primarily store and transport sulfuric acid, mix it with other raw materials for reaction, and treat tail gas.
- Granulation Equipment: You typically use a rotary drum granulator, which consists of a tilted cylindrical rotating drum, a motor, and a reducer. Raw materials and return materials are fed from the upper end of the drum. They mix with the high-temperature slurry sprayed from the tubular neutralization reactor, and granulation occurs as the drum rotates.
- Drying Equipment: You generally use a rotary kiln dryer with a counter-current drying method. It uses hot air to dry the wet fertilizer granules, transforming the liquid cross-linking inside the granules into solid cross-linking to increase their strength.
- Screening Equipment: You use vibrating screens, trommel screens, and similar equipment to screen the dried granules. The granules that meet the standard size become the final product, while you process the smaller and larger granules and return them as return materials to the front end of the granulator.
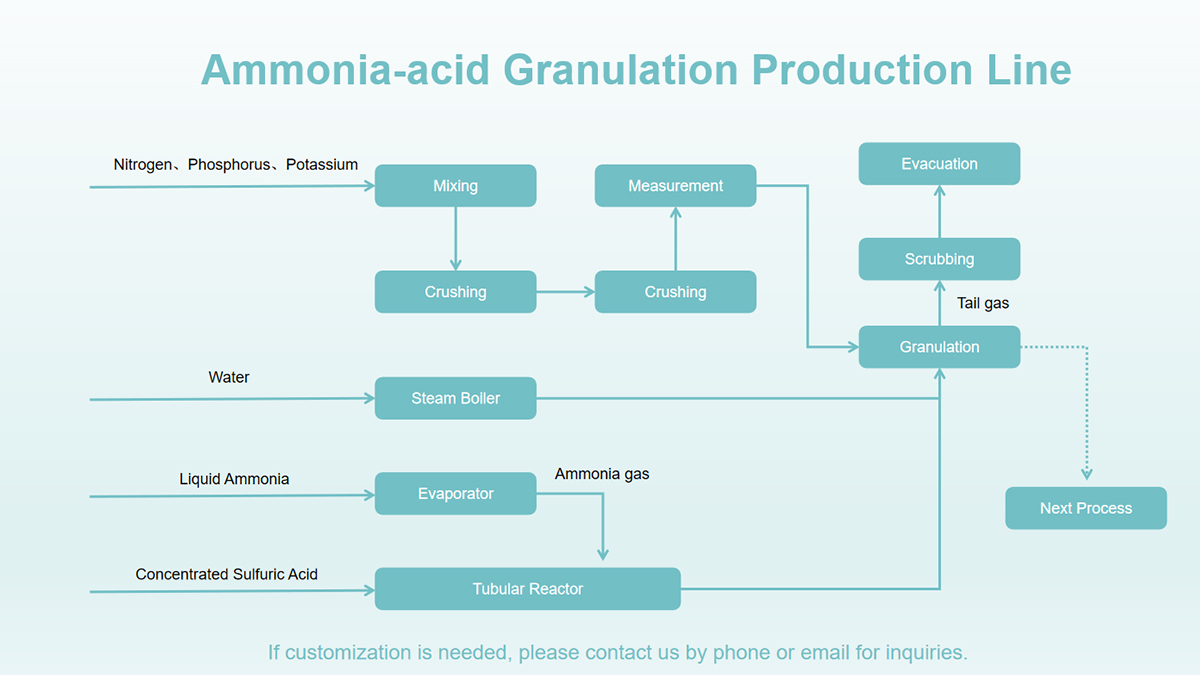
III. Process Flow
- Raw Material Preparation: You crush, screen, and meter solid raw materials like potassium chloride, monoammonium phosphate, and urea to meet the required particle size and ratio. At the same time, you store liquid raw materials like concentrated sulfuric acid in the acid station for later use.
- Granulation: The solid raw materials from the batching process and the system's return materials enter the rotary drum granulator. The liquid ammonia, after processing at the ammonia station, splits into two paths. One path reacts quickly with the diluted sulfuric acid in the tubular reactor. A spray nozzle uniformly atomizes and sprays the resulting high-temperature ammonium sulfate solution onto the material layer in the granulator. The other path vaporizes a mixture of gaseous ammonia and steam, which a mixed distributor introduces into the material layer. This continues to react with the monoammonium phosphate and superphosphate in the material layer inside the granulator. The dry and wet materials agglomerate into granules as the granulator rotates.
- Drying: You use a hoist or belt conveyor to feed the wet granular material from the granulator into a rotary dryer. It dries the material and removes moisture using hot air at a specific temperature.
- Screening: You send the dried granules to a screening machine for screening. The qualified granules enter the subsequent coating and packaging processes as finished products. You crush large return granules and return them to the granulation system with the fine powder return materials to re-enter the granulation process.
- Tail Gas Treatment: The tail gas from drying, cooling, and dust collection passes through three stages of treatment—a cyclone dust collector, gravity settling, and water bath scrubbing—before meeting emission standards, which reduces environmental pollution.
IV. Features of the Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line
The compound fertilizer ammonia-acid granulation production line is an advanced granulation process that combines ammoniation and acidolysis reactions. It offers significant advantages in fertilizer production, with its core features primarily in the following aspects:
- Energy-Efficient and Cost-Effective Process: Ammonia-acid granulation directly reacts ammonia (e.g., liquid ammonia, ammonia water) with acidic raw materials like phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid inside the granulator. It uses the large amount of heat released from the reaction to provide the necessary thermal energy for granulation, reducing dependence on external heat sources like steam. At the same time, the ammonium phosphate and ammonium sulfate products from the reaction act as a natural binder phase, reducing the amount of water you add and significantly lowering energy consumption in the subsequent drying stage (saving over 30% of energy compared to traditional rotary drum granulation). Additionally, the compact process flow and high raw material conversion rate reduce material loss, further lowering overall production costs.
- Excellent Product Quality and Stable Physical Properties: The compound fertilizer granules the production line produces are spherical or nearly spherical, with high uniformity (particle size 2-4.75mm can account for over 90%). The granules also have high strength (crushing strength ≥25N) and excellent resistance to crushing and caking, making them easy to store, transport, and apply with machinery. Because the liquid phase distributes uniformly during granulation, the nutrients mix thoroughly inside the granules. This avoids "half-cooked granules" or nutrient segregation problems common in traditional processes and ensures uniform nutrient content in the product.
- High Nutrient Concentration and Flexible Formulation: Ammonia-acid granulation allows you to flexibly adjust the basic nutrient content of nitrogen and phosphorus by controlling the reaction ratio of ammonia to acid. You can easily produce high-concentration compound fertilizers with a total nutrient content (N+P₂O₅+K₂O) of over 45%, and up to 60%. At the same time, the production line adapts to a wide range of raw materials, allowing you to combine them with various other materials like potassium chloride, potassium sulfate, and organic fertilizers. This creates a multi-element compound of "nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium-medium and trace elements-organic nutrients," meeting the specific fertilization needs of different crops and soils.
- Outstanding Environmental Performance and Reduced Pollution Emissions: The reaction efficiency of ammonia and acid in the process is high (ammonia utilization rate can reach over 95%), which greatly reduces the air pollution caused by ammonia volatilization. The production line uses a complementary tail gas scrubbing system to recover and treat the small amount of unreacted ammonia and dust, making the tail gas emission indicators (such as ammonia concentration ≤10mg/m³) much lower than national standards. In addition, the process produces minimal wastewater, and you can achieve "zero discharge" through recycling, which aligns with green chemical production requirements.
- Continuous and Stable Production with a High Degree of Automation: Modern ammonia-acid granulation production lines typically have a DCS automated control system. This system allows you to precisely and accurately control key parameters like raw material ratios, reaction temperature, granulation moisture, and particle size in real time. This ensures a continuous and stable production process and reduces human operating errors. A single production line's capacity can range from 50,000 tons/year to 600,000 tons/year, meeting the production needs of different-sized companies. The equipment also has a low failure rate and low operation and maintenance costs.
- Balanced Fertilizer Release and Improved Crop Absorption Efficiency: In the compound fertilizer produced by ammonia-acid granulation, nitrogen nutrients are primarily in the form of ammonium nitrogen, and phosphorus nutrients exist as a combination of water-soluble and citrate-soluble phosphorus. The nutrient release rate is moderate, satisfying the rapid needs of crops in the seedling stage while providing a continuous supply of fertilizer during the middle and late stages and reducing nutrient loss. Additionally, the porous granule structure benefits soil microbial activity, which can promote nutrient absorption and utilization by crops, increasing fertilizer utilization by 10-15%.
In summary, the compound fertilizer ammonia-acid granulation production line, with its energy efficiency, high-quality products, and stable environmental performance, has become a mainstream process for producing high-concentration compound fertilizers, especially for the large-scale and specialized modern agricultural fertilizer needs.
V. Application Fields of the Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line
The compound fertilizer ammonia-acid granulation production line, with the uniform nutrient, high stability, and high utilization rate of the compound fertilizers it produces, has wide applications in multiple fields.
- In Agriculture: The compound fertilizer from this production line is an important guarantee for the growth of grain crops. Take wheat as an example: this compound fertilizer plays an important role at every stage of its growth. In the seedling stage, it can slowly release nitrogen to meet the wheat's initial nutrient needs, promoting root development and seedling growth. During the tillering stage, an adequate nutrient supply can increase the number of effective tillers. In the grain-filling stage, the rich phosphorus and potassium can increase the thousand-grain weight of the wheat, thus increasing yield. For corn, the compound fertilizer can provide balanced nutrition in the seedling stage, helping the seedlings grow strong. In the grain-filling stage, adequate phosphorus and potassium can increase the corn's grain weight, improving the quality and yield of the corn. In rice cultivation, ammonia-acid granulation compound fertilizer can also meet its needs for nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other nutrients at different growth stages, promoting rice tillering, heading, and grain filling, and increasing the rice's grain setting rate.
The application of the compound fertilizer ammonia-acid granulation production line is also widespread in the cultivation of economic crops. Cotton growth requires a large amount of nutrients. The compound fertilizer produced by this production line can provide continuous nutritional support for cotton, promoting its leaf and branch growth, flowering, and boll setting, and improving its yield and fiber quality. During its growth, rapeseed has a high demand for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Ammonia-acid granulation compound fertilizer can meet its needs, helping rapeseed grow and develop and improving the yield and oil content of rapeseed. As a fertilizer-loving crop, sugarcane receives an adequate supply of nutrients from the compound fertilizer, which promotes the growth of its stalks and increases its sweetness and yield.
Vegetable cultivation cannot do without high-quality fertilizers, and the compound fertilizer produced by the ammonia-acid granulation production line performs excellently in vegetable cultivation. In tomato cultivation, it can provide balanced nutrition, promote flowering and fruiting, and improve the quality and yield of the fruit while reducing problems like deformed fruit caused by unbalanced fertilization. A cucumber's growth requires frequent nutrient supply. This compound fertilizer can continuously provide nutrients, promoting the growth of the cucumber vines and the development of the fruit, and increasing the cucumber's yield. In addition, this compound fertilizer can play a good role in the cultivation of various other vegetables like chili peppers, eggplants, and cabbages, improving the quality and yield of the vegetables.
In fruit tree cultivation, the compound fertilizer from the ammonia-acid granulation production line also holds an important position. Apple, pear, and other fruit trees need different nutrients throughout their growth cycle. This compound fertilizer can provide corresponding nutrition based on the fruit trees' growth needs, promoting their flowering and fruiting and improving the color, taste, and yield of the fruit. Citrus trees are more sensitive to nutrients, and the uniform nutrients of ammonia-acid granulation compound fertilizer can meet their needs, reducing phenomena like flower and fruit drop caused by nutrient imbalance.
- In Forestry: The cultivation of plantations also cannot do without the compound fertilizer from the ammonia-acid granulation production line. In the seedling cultivation stage, the compound fertilizer can provide adequate nutrients for the seedlings, increasing their survival rate and growth speed. For adult trees, applying an appropriate amount of this compound fertilizer can promote tree growth and increase timber yield.
- In Horticulture: You can use this compound fertilizer in both flower cultivation and lawn maintenance. In flower cultivation, it can promote flower growth and blooming, extend the flowering period, and increase the ornamental value of the flowers. When you maintain lawns, the compound fertilizer can provide balanced nutrition for the lawn grass, keeping the lawn green and lush.
- In Special Soil Environments: In special soil environments like saline-alkali land and barren soil, the compound fertilizer ammonia-acid granulation production line can produce special-formula compound fertilizers based on the characteristics of the soil. These compound fertilizers can improve soil structure, increase soil fertility, create a good environment for crop growth, and promote crop growth in special soil environments.
VI. Key Selection Points for the Ammonia-Acid Granulation Production Line
In the field of compound fertilizer production, the ammonia-acid granulation process is widely used because it can produce high-concentration, high-quality products. To select a suitable ammonia-acid granulation production line, you need to consider many factors to ensure stable and efficient production that meets environmental and quality requirements. Here are the key selection points:
- Match Production Needs: First, you must clearly define your production scale needs, including annual and daily capacity. Production lines of different scales have significant differences in equipment configuration, footprint, and investment cost. A small-scale production line may focus more on flexibility and initial investment cost, making it suitable for small-batch, multi-product production. A large-scale production line, on the other hand, needs to emphasize continuous stability and economies of scale to meet the production needs of large-batch, single or a few products. At the same time, you should consider future capacity expansion needs and choose a production line design that offers some room for expansion.
- Consider Raw Material Adaptability: Common raw materials for the ammonia-acid granulation process include urea, monoammonium phosphate, potassium chloride, and potassium sulfate. Different raw materials have different moisture content, particle sizes, and chemical reaction characteristics. The production line must adapt to the characteristics of the raw materials you choose to avoid problems like raw material sticking, equipment clogging, or incomplete reactions. For example, for high-moisture raw materials, you need to equip the line with appropriate pre-treatment equipment, such as dryers and pulverizers, to ensure the raw materials meet process requirements before entering the granulation system. You also need to consider the stability of the raw material source, and the production line's ability to adapt to different batches of raw materials is also very important.
- Ensure Process Stability: The core of ammonia-acid granulation lies in the chemical reaction inside the reactor and the granule formation process inside the granulator. Process stability directly affects product quality. The production line should have the ability to precisely control key parameters like reaction temperature, pH value, and material ratio. If the reaction temperature is too high or too low, or if the pH value control is improper, it can lead to incomplete reactions, insufficient granule strength, and uneven nutrient distribution. Choosing a production line with an online monitoring and automatic adjustment system can monitor changes in process parameters in real time and make timely adjustments, reducing human operating errors and ensuring process stability and consistency.
- Equipment Quality and Durability: The quality of the production line equipment is the foundation for stable production. The quality of key equipment such as the granulator, reactor, dryer, cooler, and screening machine is particularly important. Because the compound fertilizer production environment may contain corrosive substances (such as acidic gases from the ammonia-acid reaction), the equipment materials must have good corrosion resistance. For example, you should use stainless steel materials or apply professional anti-corrosion treatments. At the same time, the equipment's structural design should be reasonable, making it easy to operate, maintain, and service, which reduces downtime from failures. Checking the equipment manufacturer's manufacturing process, quality inspection standards, and feedback from past users can help you judge the equipment's durability.
- Energy Consumption and Environmental Compliance: In the context of increasingly strict environmental policies, the production line's energy consumption and environmental performance are important factors to consider. For energy consumption, you need to pay attention to the energy utilization efficiency of energy-consuming equipment such as dryers and hot air furnaces. Choose energy-saving equipment to reduce the cost of energy consumption like coal, electricity, and water. For environmental protection, the production line must have effective dust, waste gas, and wastewater treatment systems. Granulation, drying, and screening processes generate dust, so you must install efficient bag dust collectors or electrostatic precipitators. The ammonia-acid reaction may generate waste gases like ammonia gas, which you must treat with equipment like absorption towers to ensure waste gas emissions comply with national standards. You also need to treat the small amount of wastewater produced during the production process to meet discharge standards or recycle it.
- Automation and Intelligence Level: A higher level of automation and intelligence can improve production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance product quality stability. Choose a production line with a PLC control system and a human-machine interface. This can achieve automated control of the production process, including automatic linkage of raw material metering, conveying, reaction parameter adjustment, and finished product packaging. Intelligent functions like remote monitoring, data collection and analysis, and fault warnings can help managers grasp the production status in real time, discover and solve problems promptly, and optimize the production process.
- After-Sales Service and Technical Support: A compound fertilizer ammonia-acid granulation production line has complex equipment, and its installation, debugging, and maintenance require professional technical support. Choosing a manufacturer with good after-sales service and technical support capabilities is crucial. The manufacturer should provide equipment installation guidance and debugging services to ensure the production line starts up smoothly. They should provide comprehensive technical training so operators master equipment operation and daily maintenance skills. During the equipment's operation, they should be able to respond to maintenance needs in a timely manner and provide a sufficient supply of spare parts to reduce downtime losses due to equipment failures. In addition, the manufacturer's R&D capabilities are also important, as they can support the production line's technical upgrades and process improvements.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: You should conduct a cost-benefit analysis by comprehensively considering the production line's initial investment, operating costs, maintenance costs, and product revenue. The initial investment includes not only the cost of equipment but also the costs of factory construction, equipment installation, and auxiliary facilities. Operating costs involve energy consumption, raw material consumption, and labor costs. When you choose, do not just pursue a low price. Instead, you should comprehensively evaluate factors like equipment quality, performance, energy consumption, and environmental protection to choose a production line with a high-cost performance. At the same time, you should consider how the production line's production efficiency affects product costs. An efficient and stable production line can reduce the cost per unit of product, increasing your market competitiveness.
- Product Quality Assurance: The production line must be able to stably produce compound fertilizer products that meet quality standards, including granule strength, particle size uniformity, moisture content, and nutrient content and uniformity. The granulator's performance directly affects granule quality, so you should choose a granulator with good granulation results and high granule uniformity. The screening system must effectively separate unqualified granules to ensure the finished product's particle size meets requirements. In addition, the production line should have the conditions or interfaces for product quality testing to facilitate timely testing of the finished product and ensure stable and reliable product quality.
- Site and Environment Adaptability: Based on your company's factory site conditions, choose a production line with a suitable layout. Consider the production line's footprint, the spacing between equipment, and the material conveying paths to ensure a reasonable layout of the production site that facilitates operation and material flow. At the same time, you should consider the impact of the production environment on the production line, such as the factory's ventilation, lighting, temperature, and humidity conditions. Take corresponding measures when necessary to ensure the production line's normal operation and the safety of the operators' working environment.
- Industry Cases and Reputation Reference: Understand the actual operation of different brands or models of ammonia-acid granulation production lines used by other companies in the same industry. Refer to their usage experience and reputation. Choosing an equipment manufacturer and production line model with a good reputation and many successful cases in the industry can reduce selection risks. You can obtain more information about the production line's performance and usage results through industry exhibitions, technical exchange meetings, and company visits.
In short, selecting an ammonia-acid granulation production line is a systematic project. You need to comprehensively consider many factors, including production needs, raw material characteristics, process stability, equipment quality, energy consumption and environmental protection, automation level, cost-effectiveness, and also the manufacturer's after-sales service and industry reputation. Only then can you choose the most suitable production line for your company's actual situation and provide a strong guarantee for your company's production and operation.
Tai'an Hongxin Environmental:
Supply of High-Quality and Efficient Fertilizer Production Equipment, Straw Processing Equipment, Waste Treatment Equipment and Mining Equipment. If you are looking for fertilizer production equipment and production lines, feel free to contact us at any time.- Whatsapp(Tel): + 86 139-0548-5429( Mr. Li)
- E-mail: tahongxin@gmail.com